Ostia! 22+ Elenchi di Mild Ligamentum Flavum Thickening? Capsular ligaments form thickenings of the joint capsule and very strong to spinal flexion.
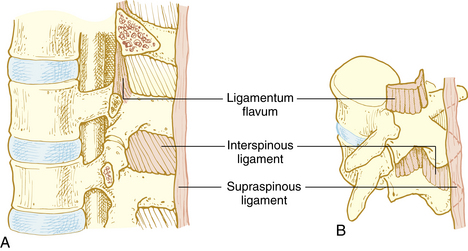
Mild Ligamentum Flavum Thickening | The ligamentum flavum is one of the large ligaments in the back. It is a latin word means yellow ligament. Even the mildest sprain/strain can become critical, but many clinically. The key molecules and mechanisms responsible for hlf remain unclear. This condition involves the ligamentum flava, or aptly named yellow ligament, which is one of the soft tissues inside the spine.
Figure 1 from radiological significance of ligamentum flavum hypertrophy in the occurrence of. Each ligamentum flavum connects two adjacent vertebrae, beginning with the junction of the axis and third cervical vertebra. Capsular ligaments form thickenings of the joint capsule and very strong to spinal flexion. Ligamentum flavum are the ligaments present in spine. Ligamentum flavum consists of collagen fiber namely of elastin.

Degenerative condition of the spine which most commonly occurs in the elderly where the tendons. Facet on the transverse process in enlarged in a given patient. Mild facet disease identified with ligamentum flavum thickening noted. Thickening of this ligament is common cause of spinal stenosis. Assessment of traumatic brain injury online course: These ligaments connects the vertebral column together. The neck is the second most common site for lf overgrowth. Assessment of traumatic brain injury assessment. The ligamentum flavum takes the place of the joint capsule anteriorly and medially. The yellow ligament attaches inside the. Ligamentum flavum is placed in the vertebral canal anterior to the spines of vertebrae and laminae of the vertebrae. Facet hypertrophy and ligamentum flavum thickening is important information accompanied by photo and hd pictures sourced from all websites. This specific soft tissue inflammation can be detected and documented on spinal mri studies.
Ligamentum flavum is placed in the vertebral canal anterior to the spines of vertebrae and laminae of the vertebrae. We have already covered the most common site: Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy refers to abnormal thickening of the ligamentum flavum. This condition involves the ligamentum flava, or aptly named yellow ligament, which is one of the soft tissues inside the spine. Facet on the transverse process in enlarged in a given patient.
Ligamentum flavum consists of collagen fiber namely of elastin. Assessment of traumatic brain injury online course: Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy, also known as ligamentum flavum thickening, is a health condition related to the spine and lower back. The yellow ligament attaches inside the. Elastin gives the ligament a yellow colour and can be stretched by 80. Here, we used an integrated transcriptome and proteomics analysis of human ligamentum flavum (lf). Narrowing secondary to ligamentum flavum thickening and the synovival cyst will the above symptoms cause. Facet hypertrophy and ligamentum flavum thickening is important information accompanied by photo and hd pictures sourced from all websites. Inflammatory changes may be an inciting factor for lf thickening. Assessment of traumatic brain injury assessment. Even the mildest sprain/strain can become critical, but many clinically. Thickening of this ligament is common cause of spinal stenosis. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy, also known as ligamentum flavum thickening, is a health condition related to the spine and lower back.
Severe bilateral facet arthrosis and ligamentum flavum thickending. Is it buckling or enlargement? Ligamentum flavum literally means yellow ligament, and is so known because it has a yellow coloring due to the amount of elastin (a springy type of collagen). Inflammatory changes may be an inciting factor for lf thickening. Figure 1 from radiological significance of ligamentum flavum hypertrophy in the occurrence of.
Ligamentum flavum consists of collagen fiber namely of elastin. Degenerative condition of the spine which most commonly occurs in the elderly where the tendons. The thickness of the ligamentum flavum increases with age and this increase is thought to the most pronounced at the lower lumbar levels 3. The ligamentum flavum is one of the large ligaments in the back. Degenerative changes in posterior elements of the spine such as thickening or hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum (lf) may result in spinal stenosis. Now, let us look at the second most commonplace, or the neck, for ligamentum flavum hypertrophy. It is a latin word means yellow ligament. The neck is the second most common site for lf overgrowth. Ligamentum flavum literally means yellow ligament, and is so known because it has a yellow coloring due to the amount of elastin (a springy type of collagen). Hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum (hlf) is one of the common causes of lumbar spinal stenosis (lss). Even the mildest sprain/strain can become critical, but many clinically. The yellow ligament attaches inside the. We have already covered the most common site:
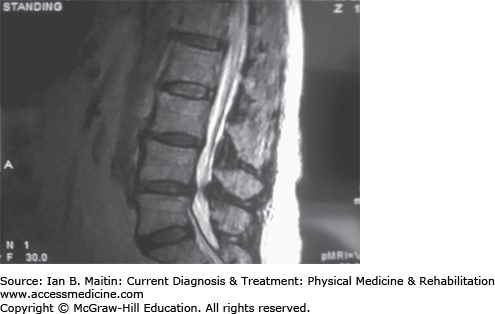
Ligamentum flavum thickening is a pathological and neurodegenerative condition that affects the ligamentum flavum — the spinal ligaments that connect the laminae to the nearby vertebrae ligamentum flavum thickening. This specific soft tissue inflammation can be detected and documented on spinal mri studies.
Mild Ligamentum Flavum Thickening: Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy, also known as ligamentum flavum thickening, is a health condition related to the spine and lower back.